 Trade Data Provider
Trade Data Provider
 2024-05-30
2024-05-30
In the competitive world of global trade, making informed decisions about suppliers is crucial for business success. Shipment data is a valuable resource that can provide insights into supplier performance, market trends, and supply chain reliability. Here's how you can use shipment data to choose a global supplier effectively.

1. Understand Shipment Data
a. What is Shipment Data?
Shipment data includes information about the movement of goods from one location to another. This data typically covers details such as the type of product, quantity, shipment dates, origin and destination ports, shipping companies, and sometimes the involved parties.
b. Sources of Shipment Data
Shipment data can be sourced from various places, including:
- Customs databases
- Import/export records
- Trade data platforms like Tendata
- Industry reports and market analysis
2. Identify Potential Suppliers
a. Use Shipment Data Platforms
Platforms like Tendata allow you to search for specific products and view detailed shipment records. This can help identify companies that frequently export the goods you need.
b. Analyze Export Volume
Look for suppliers with a high volume of exports. A higher volume generally indicates a reliable and experienced supplier capable of handling large orders.
c. Check Export Destinations
Examine the destinations to which the suppliers are exporting. If they export to multiple countries, it suggests they are well-versed in international shipping regulations and logistics.
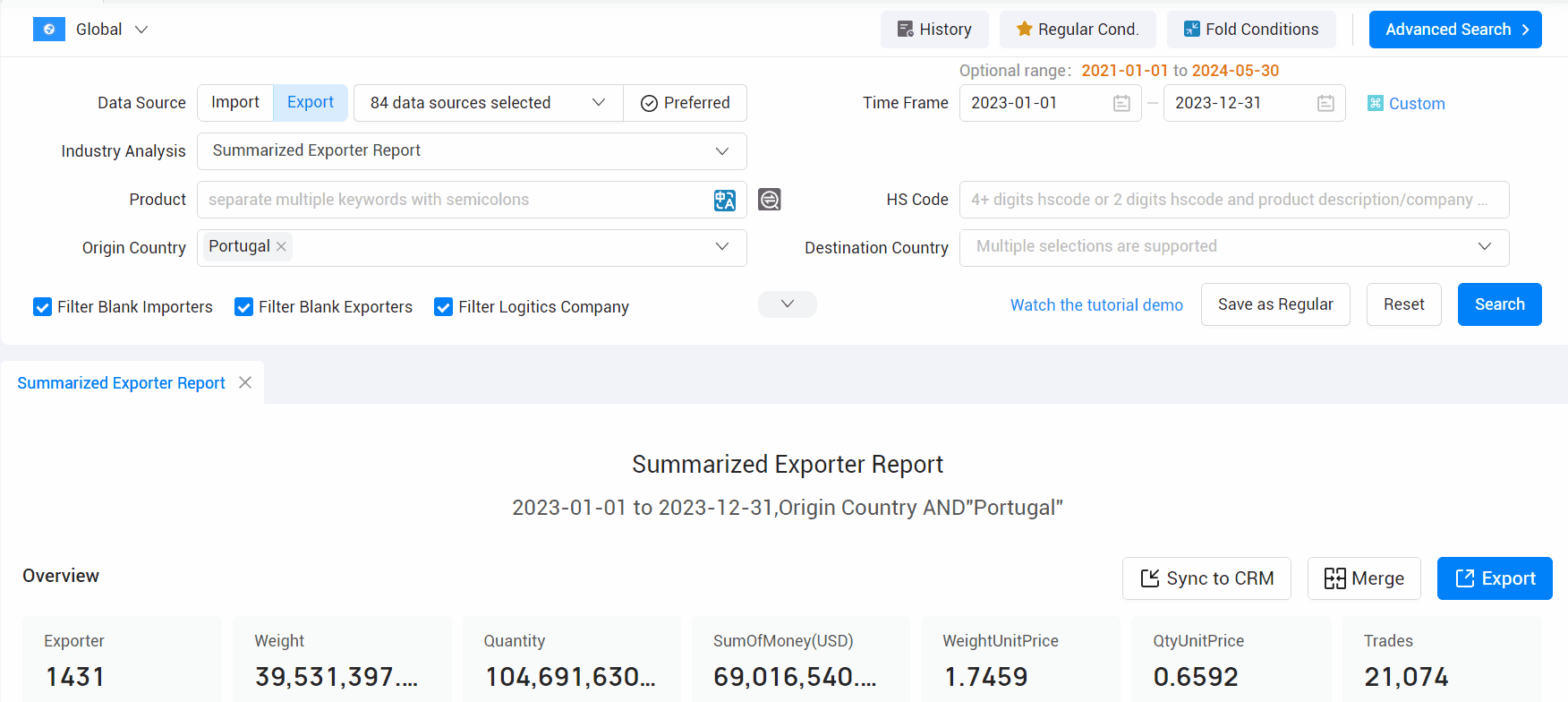
3. Evaluate Supplier Performance
a. On-Time Shipments
Review the shipment data to see if the supplier consistently meets delivery deadlines. Frequent delays can be a red flag indicating potential supply chain issues.
b. Product Quality
While shipment data itself may not directly reveal product quality, you can cross-reference with customer reviews, feedback, and any available inspection records to assess the quality of goods supplied.
c. Repeat Customers
Suppliers with a high number of repeat customers are often more reliable and trusted in the market. This information can sometimes be inferred from shipment data.
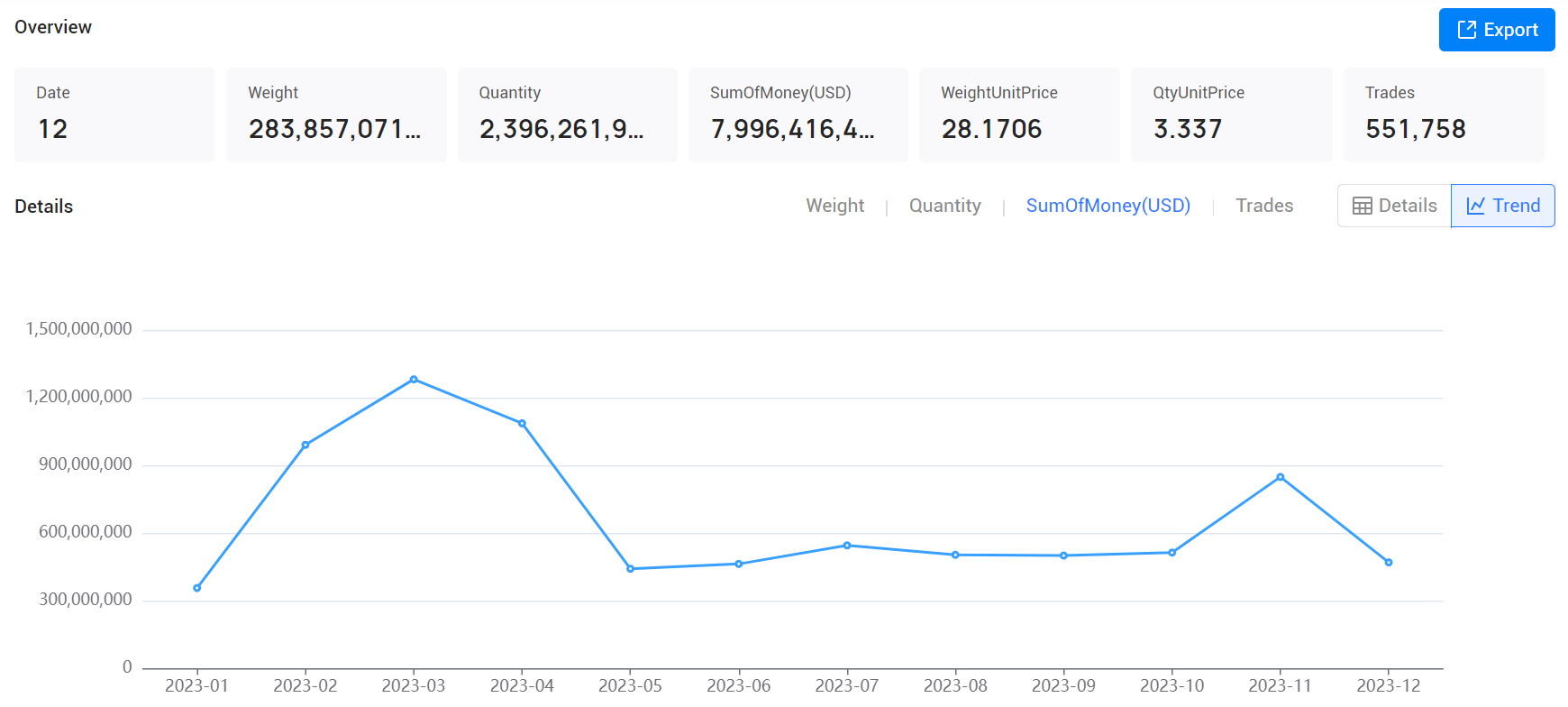
4. Analyze Market Trends
a. Seasonal Trends
Use shipment data to identify seasonal trends in supply and demand. This can help you plan your orders better and negotiate favorable terms with suppliers during off-peak seasons.
b. Emerging Markets
Look for trends indicating growing markets for your products. Suppliers who are expanding into new markets might be more innovative and flexible, providing you with additional opportunities.
5. Verify Compliance and Certifications
a. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Check if the suppliers comply with international trade laws and regulations. Shipment data can sometimes reveal compliance with standards such as ISO certifications, environmental regulations, and other industry-specific standards.
b. Ethical Sourcing
Review the shipment data for information on ethical sourcing practices. Suppliers who ship to countries with strict labor and environmental laws are more likely to adhere to ethical practices.
6. Assess Financial Stability
a. Shipment Consistency
A consistent shipping record over time can indicate a supplier’s financial health and stability. Frequent fluctuations might suggest financial difficulties or operational issues.
b. Market Presence
Suppliers with a broad market presence are generally more stable and less likely to face financial troubles. Shipment data showing exports to multiple countries can be a positive indicator.
7. Negotiate Terms
a. Leverage Data in Negotiations
Use the insights gained from shipment data to negotiate better terms with potential suppliers. Highlight your awareness of market rates, shipping costs, and supply chain efficiencies to secure favorable agreements.
b. Establish Clear KPIs
Set clear key performance indicators (KPIs) based on shipment data, such as on-time delivery rates, shipment accuracy, and order volumes. This ensures that your supplier meets your standards and performance expectations.
8. Monitor Supplier Performance
a. Continuous Monitoring
Regularly review shipment data to monitor supplier performance over time. This helps you identify any potential issues early and address them promptly.
b. Performance Reviews
Conduct periodic performance reviews with your suppliers, using shipment data to back up your assessments and discuss areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Using shipment data to choose a global supplier can significantly enhance your decision-making process by providing valuable insights into supplier performance, market trends, and compliance. By leveraging platforms like Tendata and analyzing detailed shipment records, you can identify reliable suppliers, negotiate better terms, and ensure a smooth and efficient supply chain for your business.
Customs data contains a vast amount of information, and extracting relevant customer contact information can be time-consuming, with results not always meeting expectations. Is it truly the case, or is it because customs data is being used incorrectly, resulting in wasted effort and time?
Utilizing customs data for customer development can be achieved by precisely characterizing all buyers and their procurement systems in the target market. This allows for the quick identification of the most compatible customers, discerning their credit systems and procurement information, determining high-quality customers and profit margins, enhancing development efficiency, and improving overall effectiveness.
In customs data, one can observe the suppliers of buyers. Some of these suppliers are trade companies and also potential customers. In-depth analysis can be conducted on these trade companies, and key customers can be selected for focused development. Information such as buyer contacts, trade partners, procurement cycles, and purchase volumes can be obtained. While customs data may lack contact information due to being derived from bill of lading information, Tendata iTrader provides not only customs data but also business and internet data. This allows for the direct extraction of contact information and positions based on buyer names, making customer development through customs data seamless. (>>> Click To Get Free Demo for Customs Data From 90+ Countries) For new customer development using customs data, three strategies are available for consideration.
1. Establishing a Customer Database by Country:
Building a customer database is akin to maintaining a work record. Start by using trade tracking features to compile a list of all customers in a country. Analyze each buyer's purchase volume, procurement cycle, product specifications, and supplier system. Finally, filter out 30% of the potential high-quality customers from this country and record them in your customer database, allowing flexible settings by country, time, customer name, follow-up steps, contact phone, email, contact person, etc. (>>> Click For Free Customer Development)
2. Establishing a Customer Database by Peer Companies:
Have a clear understanding of the names of peer companies (including full names, abbreviations, etc.). Use the global supplier network feature to gather all customers of these peers in the system. Analyze these customers based on purchase volume, procurement cycle, and product models. Finally, filter out key customers from your targeted peers and record them in your customer database. (>>> Click For Free Trial Application)
3. Identifying Newly Appeared Customers in Each Country:
Utilize the trade search function to select a country, set date ranges, limit product names or customs codes, and check "latest." The search results will display high-quality customers that have recently appeared in that country during the specified time period. Since these customers are newly emerging, they may have unstable supplier relationships, requiring focused follow-up. Record these new potential buyers in your customer database. (>>> Click For Free Demo Application)
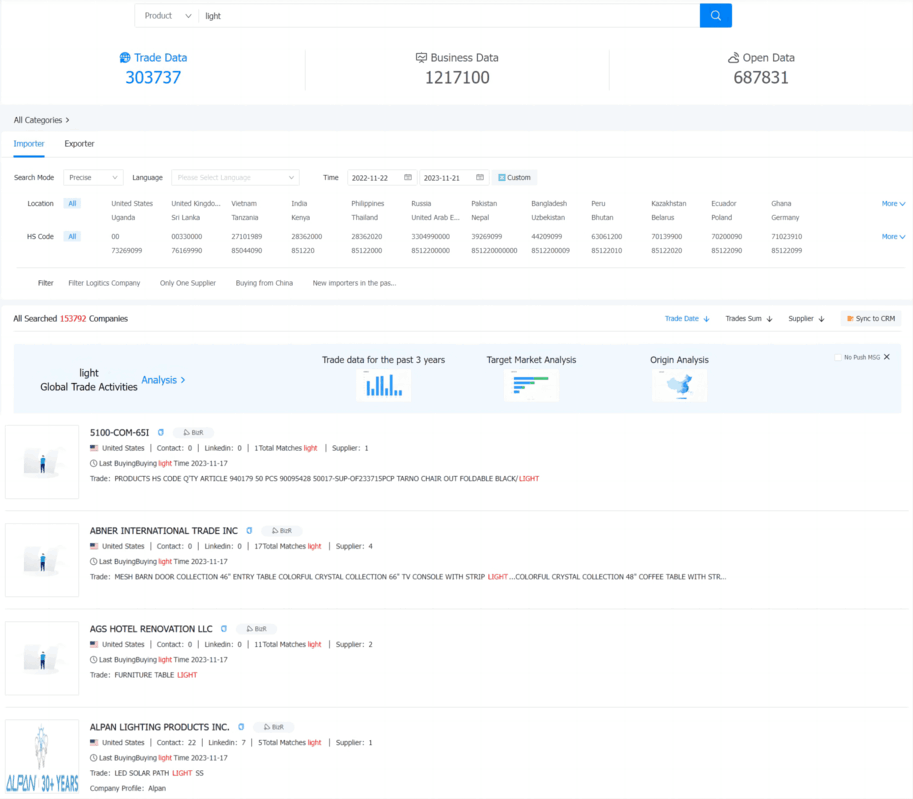
These three approaches for customer development using customs data can be implemented based on the actual needs of the company. Considering market conditions, industry characteristics, strategic requirements, etc., find a method that suits your preferences. The ultimate goal is to establish and organize a categorized archive of high-quality customers. Once suitable customers are identified, the next step is to make precise contact through various channels such as phone calls, email communication, online chat, etc.
Category
Leave Message for Demo Request or Questions


 T-info
T-info T-discovery
T-discovery

 My
Tendata
My
Tendata Market Analysis
Market Analysis Customer
Development
Customer
Development Competitor
Monitoring
Competitor
Monitoring Customer Relationship
Customer Relationship





































































































































