 Trade Data Provider
Trade Data Provider
 2025-01-10
2025-01-10
In today's globalized business environment, leveraging data is crucial for gaining a competitive edge. One of the most valuable yet often overlooked data sources is customs data. This data provides in-depth insights into international trade activities, including transaction volume, product categories, suppliers, pricing trends, and trade routes. In this article, Tendata explore Pros and Cons of customs data ,and suggest platform to help you make the most of this valuable resource.

Key Advantages of Customs Data
1. Market Research and Entry Strategy
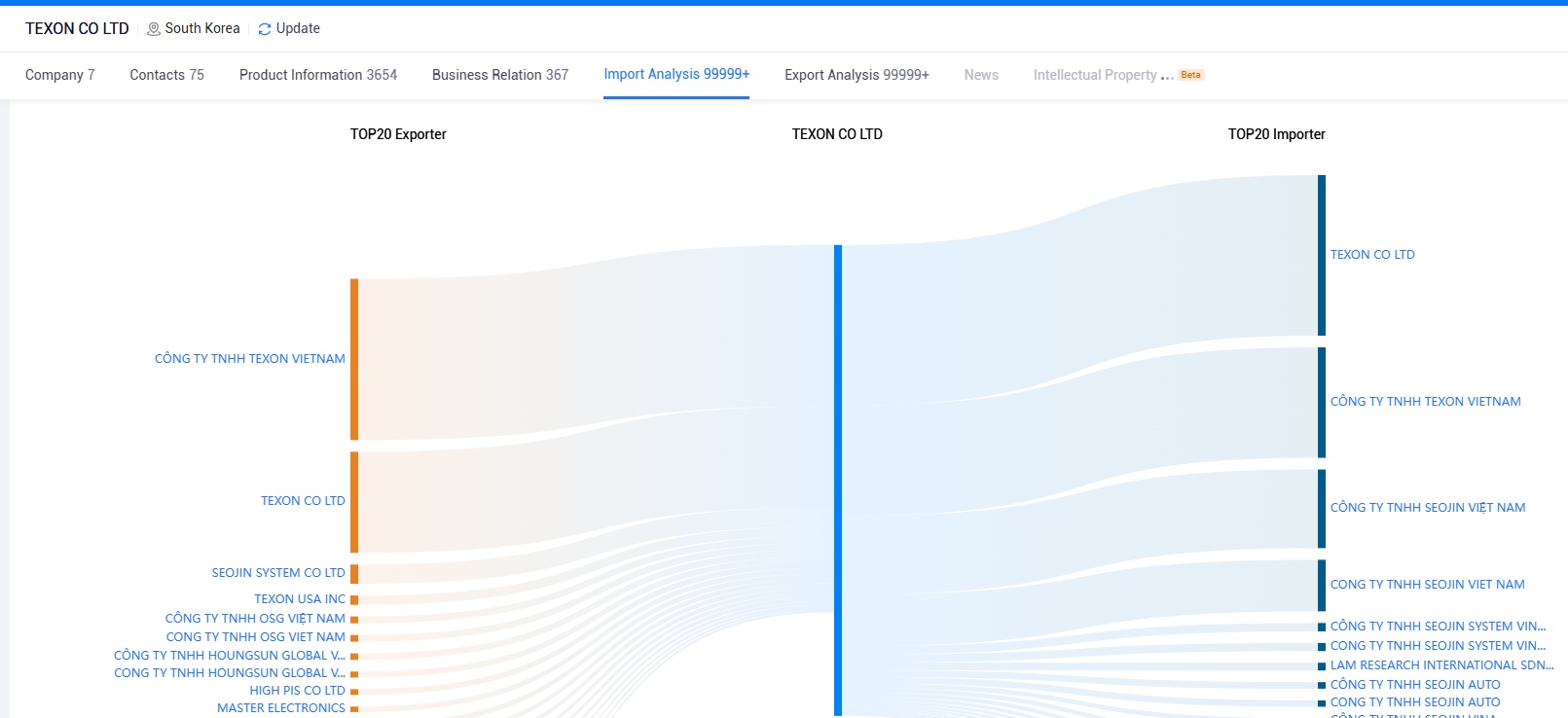
Customs data offers valuable insights into trade patterns, helping businesses understand where demand for their products exists. By analyzing import/export volumes, businesses can identify regions with growing demand for specific goods and tailor their market entry strategies accordingly. For example, if a company is exporting electronics, they can analyze which countries are importing these products in large quantities, allowing them to prioritize their expansion efforts.
2. Competitive Intelligence
One of the strongest benefits of customs data is the ability to track competitors. By monitoring the import/export activities of competitors, businesses can gain insight into their market presence, strategies, and pricing structures. This helps companies stay ahead by adjusting their own strategies in response to competitors' movements. For example, if a competitor is ramping up imports in a particular region, this could signal an impending product launch, prompting you to adjust your strategy.
3. Pricing Strategy
Customs data also aids in pricing decisions. By examining the prices at which similar products are traded in different regions, businesses can adjust their pricing strategy to be more competitive in those markets. Understanding local pricing trends ensures that companies can offer products at competitive rates without sacrificing profitability.
4. Supply Chain Optimization
Monitoring customs data helps businesses better understand global supply chains, from identifying potential suppliers to assessing risks associated with specific routes or regions. By analyzing the data, companies can find new suppliers or partners and even adjust their logistics strategies to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and minimize disruptions.
Key Challenges with Customs Data
1. Data Incompleteness
Despite its global coverage, customs data may not always be complete or entirely accurate. Different countries have different standards for reporting, which can lead to inconsistencies in the data. Additionally, some countries may not release data promptly or may have gaps in the information provided, making it difficult for businesses to rely entirely on customs data.
2. Complex Interpretation
Customs data is often raw and unfiltered, requiring expertise in data analysis to extract valuable insights. Without the necessary tools or knowledge, businesses may find it difficult to interpret and utilize this data effectively, potentially missing out on critical opportunities.
3. Legal and Privacy Issues
Customs data may sometimes contain sensitive information, such as details about suppliers or customers. While this data is often publicly available, its usage could be subject to legal restrictions depending on the country. Businesses need to be mindful of these privacy and legal issues when analyzing and using customs data for strategic decisions.
4. Timeliness of Data
Another challenge is the timeliness of customs data. Since customs data is updated periodically, there can be a lag between the actual trade activity and the data being made available. This time delay can affect decision-making, especially in industries where rapid changes in market conditions occur.
>>Contact to Try Online Demo<<
Platforms for Accessing Customs Data
UN Comtrade: comtrade.un.org
· Provides free access to international trade data from the United Nations. It covers a vast range of trade statistics and is updated annually.
Tendata: tendata.com/data
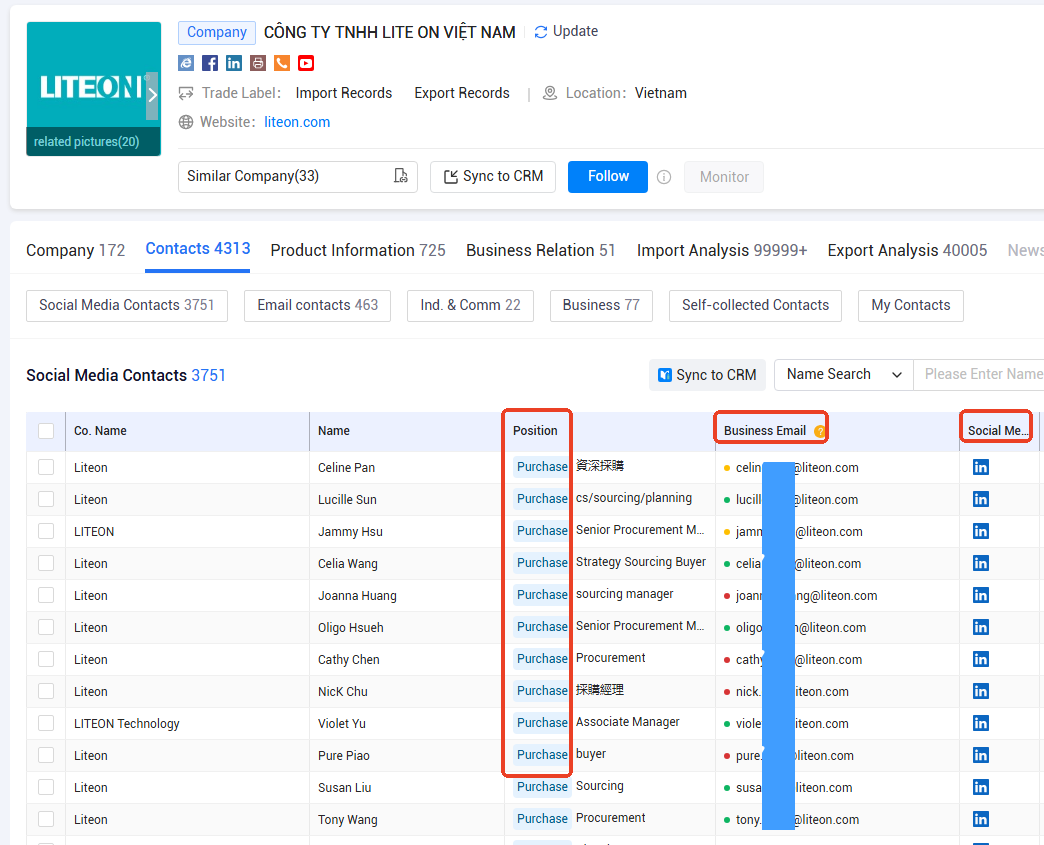
· has 210 million global enterprise information for over 218 countries, 700 million executives, decision makers contact information, including email, phone, social media, etc.. Also provides 19 visualization reports to help accurately locate and analyze the market.
World Bank – WITS (World Integrated Trade Solution): wits.worldbank.org
· Free platform provided by the World Bank that allows access to trade and tariff data from multiple sources, including the UN and the WTO. The platform is user-friendly and offers downloadable datasets.
Eurostat: ec.europa.eu/eurostat
· Statistical office of the European Union, offers free access to trade data between EU member states and non-EU countries. It provides both import/export data as well as detailed product-level trade information.
TradeMap (ITC): trademap.org
· Managed by the International Trade Centre (ITC), and offers free access to trade statistics for over 220 countries.
Conclusion
Customs data is an essential tool for businesses looking to expand their presence in global markets, optimize their supply chains, and make informed decisions about pricing and market strategies. While there are challenges associated with data completeness, interpretation, and legal considerations, these can be mitigated by using a reliable platform like Tendata. By tapping into the power of customs data, businesses can stay ahead of the competition, improve operational efficiency, and uncover new opportunities for growth in international trade.
Category
Leave Message for Demo Request or Questions


 T-info
T-info T-discovery
T-discovery

 My
Tendata
My
Tendata Market Analysis
Market Analysis Customer
Development
Customer
Development Competitor
Monitoring
Competitor
Monitoring Customer Relationship
Customer Relationship





































































































































